testicular torsion diagnosis test|is testicular torsion obvious : exporter exporters exporting Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Resultado da Verificação de segurança. Seu IP fez diversas tentativas de acessos suspeitos a sites hospedados conosco. Para liberar o acesso, responda .
{plog:ftitle_list}
A Ferramenta de busca e análise de criativos e funis de vendas, a solução completa integrada com algoritmos poderosos de inteligencia artificial para te entregar de .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
Another way to diagnose testicular torsion is by checking for the cremasteric reflex by pinching or stroking the inner thigh on the affected side. Normally, this reflex causes the testicle to contract and rise, but it is often .Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
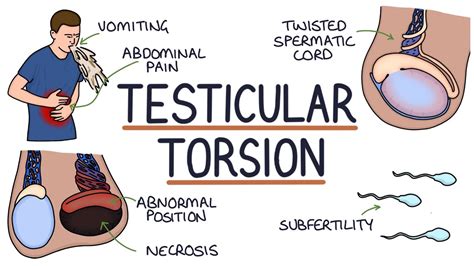
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Ultrasonography. Doctors may diagnose the condition based on a description of the symptoms and the physical examination findings. Alternatively, doctors may use imaging, usually ultrasonography, for diagnosis. Treatment of Testicular . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal . laboratory test results Hard mass within testicle Systemic symptoms (if .
Compared to testicular torsion, symptoms may be more insidious with pain persisting for days to months. Most cases occur between the ages of 18 to 35 years. Concurrent symptoms such as dysuria, hematuria, urinary urgency, fever, and tachycardia are frequently encountered. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with .
However, this test cannot reliably distinguish testicular torsion from other causes of testicular pain. . Surgical exploration can confirm the diagnosis of testicular torsion. Timing is essential as torsion for greater . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose torsion. In this examination, the doctor lightly rubs or pinches the .American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.
Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of . A history and physical examination consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical examination suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Usually affects young males but may affect males of .
The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound (Fig. 4) can be used to investigate potential compromised blood flow to the testis (if available, this test has a high sensitivity (89% . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. . Tests that can be used to .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility.
Urine and blood tests. Samples of your urine and blood may be sent to the lab for testing, too. Ultrasound. This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of your testicles. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow.Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies
If history and physical exam suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Intraoperative photograph showing extravaginal torsion of the spermatic cord and the necrotic testis in a newborn with discoloration of the right testicle at birth The diagnosis is mostly clinical, based on the presentation of the signs and symptoms of testicular torsion. These include severe pain in the scrotum and lower abdomen on the side of the affected testis, tender lumps in .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of acute scrotal disease in children, and results in an orchiectomy rate of 42% in boys undergoing surgery fo . Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .Signs and symptoms of testicular torsion include: Scrotal or testicular pain, often severe, that develops suddenly; Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting . "Six hours is not much time to get to the hospital, have the necessary diagnostic tests and get into surgery." Delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to testicular loss, which has lasting .
The symptoms of testicular torsion can seem like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his healthcare provider, or is seen in the emergency department, for a diagnosis. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. Diagnosis of testicular torsion. In patients where there is a high index of suspicion for torsion, urgent surgical consultation should not be delayed by diagnostic imaging. Our experts recommend parallel expert consultation and ultrasound imaging when feasible. . Now test your knowledge with a quiz. Take Quiz By Anton Helman | 2024-07-30T21 . The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
Tests & investigations. Information and guidance about tests and an easy, fast and accurate symptom checker. Tests & investigations. . Testicular torsion symptoms. The typical symptom of torsion of the testicle (testis) is severe pain that develops quickly - within a few hours, often much more quickly. The pain might be in the lower abdomen .A history of trauma does not exclude the diagnosis of testicular torsion. Scrotal trauma incurred during sports activities or rough, boisterous play often causes severe pain of short duration. Diagnosis Clinical presentation; Ectopic testis: Absence of a testis in the scrotum: . Testicular torsion: Acute onset of pain with a high-riding testis, swelling, very tender: Varicocele:How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time. What .
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing what is .
testicular torsion signs on examination
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
Hi. My name is Einar Egilsson and I created this online versio.
testicular torsion diagnosis test|is testicular torsion obvious